Enable Suspect Commits & Stack Trace Linking
This feature is only applicable for error issues. Other categories of issues (such as, performance issues) do not support this feature.
Sentry uses commit metadata from your source code repositories to help you resolve your issues faster. This is done by suggesting suspect commits that might have introduced an error right in your Issue Details page. It also allows Sentry to display suggested assignees — the list of the authors of those commits — and suggest their assignment to resolve the issue.
Now that you've created a release, you can tell Sentry which commits are associated with this latest version of your code; this is called commit tracking.
Step 1: Integrate your GitHub account and repositories
To integrate GitHub with your Sentry org, follow the instructions in our GitHub documentation.
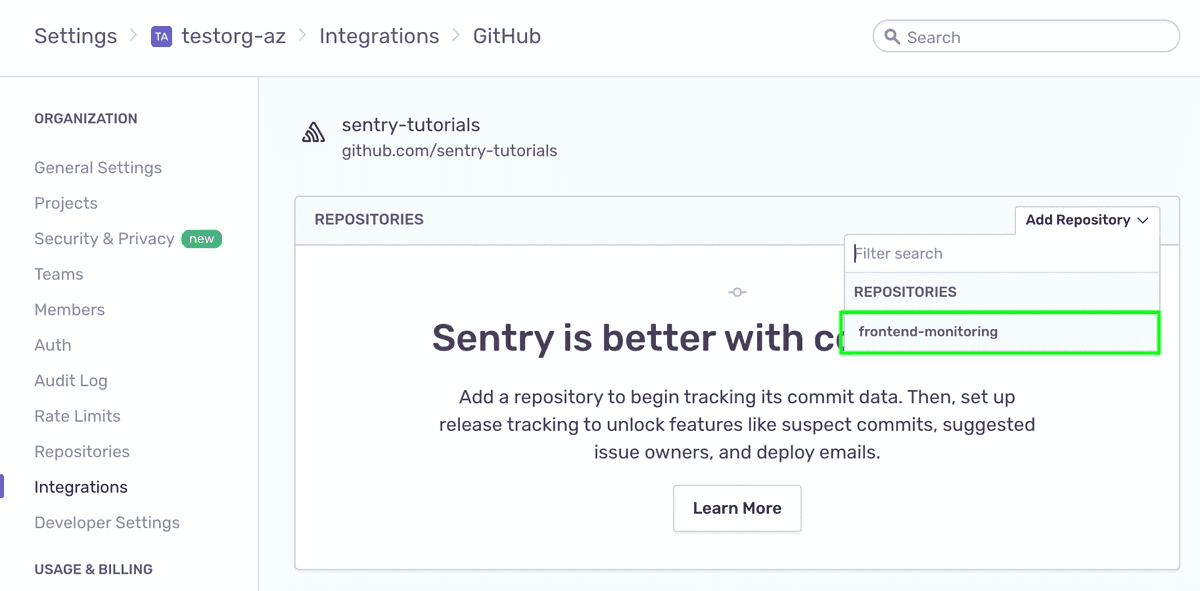
Add the
frontend-monitoringrepository from your GitHub account.Click the "Code Mappings" tab
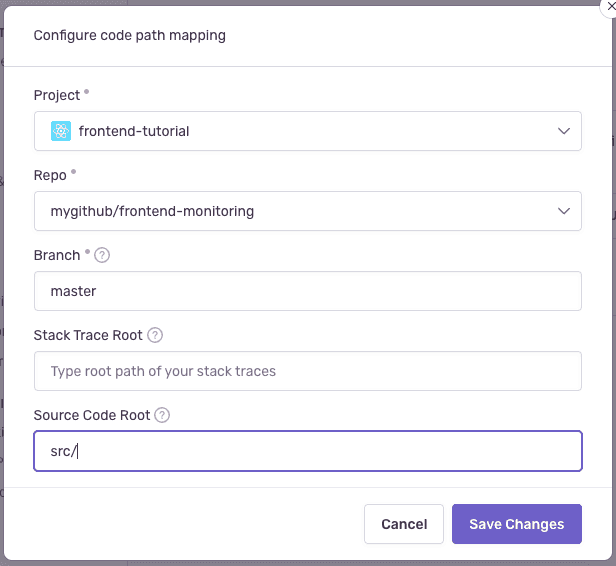
Add a code mapping between the
frontend-monitoringrepository and your Sentry project and themainormasterbranch depending on your repository. Tell Sentry that your components live in thesrc/directory:
Step 2: Set commit tracking
Now that you've set up releases in Sentry as part of your CI/CD process and integrated your source code repositories, you can associate commits from your linked repository to your releases.
In the demo project, we use a Makefile to handle our build-related tasks. If you are not using the provided React demo code and do not have a Makefile, you can run the sentry-cli commands used in this tutorial directly from the command line or integrate the commands into the relevant build script.
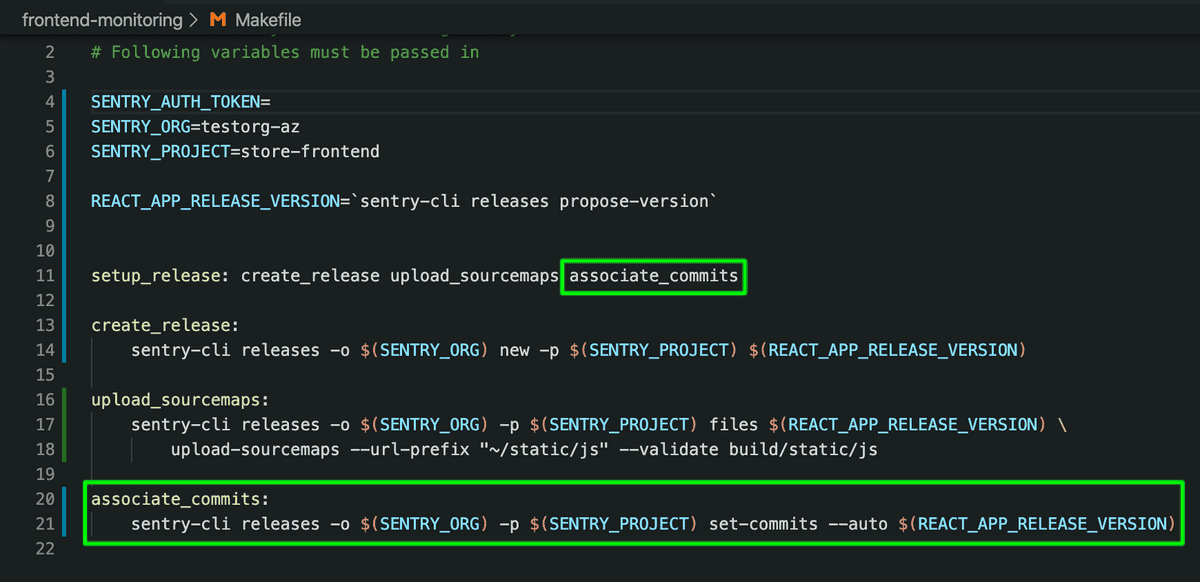
Open the
Makefilein your project.Add the following target at the bottom of the file:
Copiedassociate_commits: sentry-cli releases -o $(SENTRY_ORG) -p $(SENTRY_PROJECT) set-commits --auto $(REACT_APP_RELEASE_VERSION)The command associates commits with the release. The auto flag automatically determines the repository name, and associates commits between the previous release’s commit and the current head commit with the release.
The new target,
associate_commits, will be invoked as part of thesetup_releasetarget. Add it at the end:Copiedsetup_release: create_release upload_sourcemaps associate_commitsYour
Makefileshould look like this:If your terminal is still serving the demo app on localhost, press
^Cto shut it down.Build, serve, and restart the project on your localhost by running:
Copied> npm run deploy
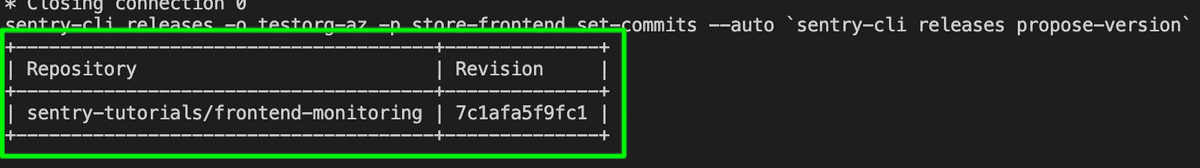
In the terminal log, notice that the
sentry-cliidentified the GitHub repository.
Step 3: Suspect commits and suggested assignees
Now suspect commits and suggested assignees should start appearing on the Issue Details page. Sentry determines these using files observed in the stack trace, authors of those files, and ownership rules.
Refresh the browser and generate an error by adding products to your cart and clicking "Checkout".
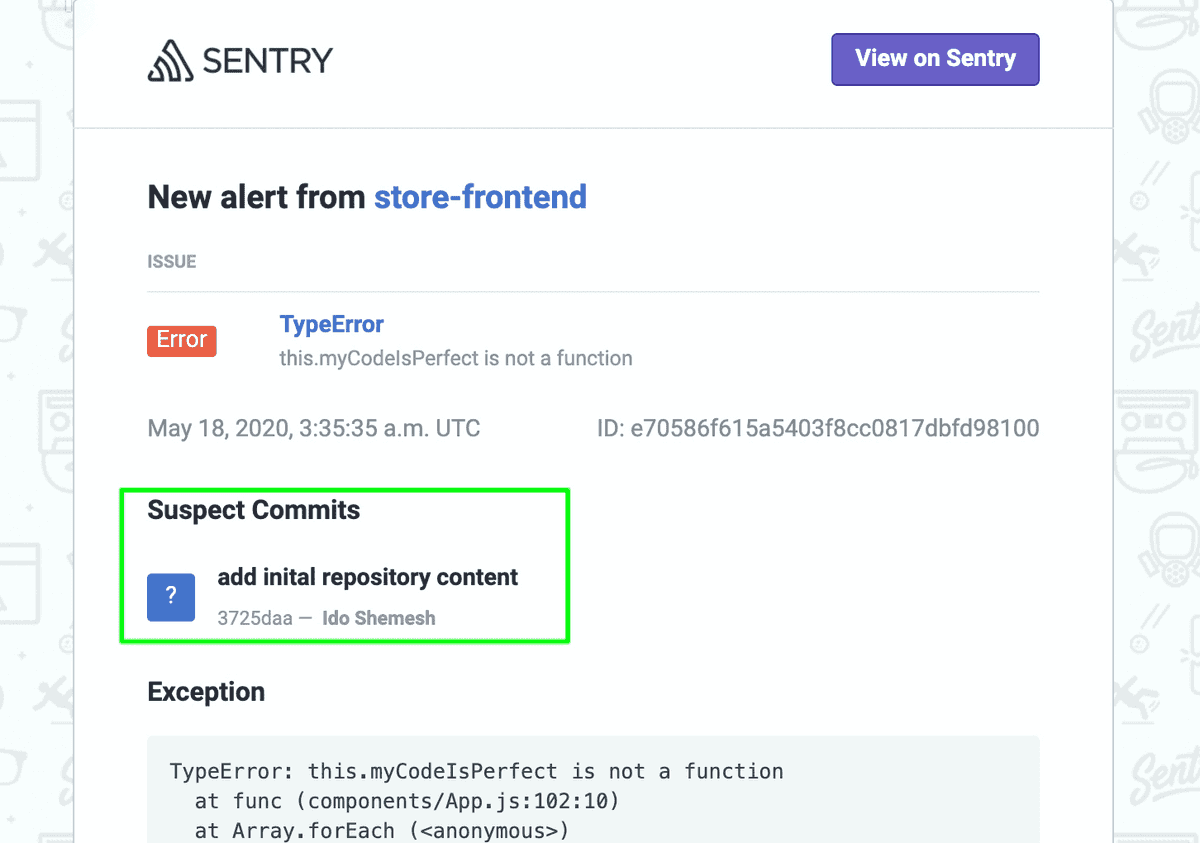
Check your email for the alert about the new error. Notice that a new "Suspect Commits" section has been added to the email.
Click "View on Sentry" to open the Issue Details page.
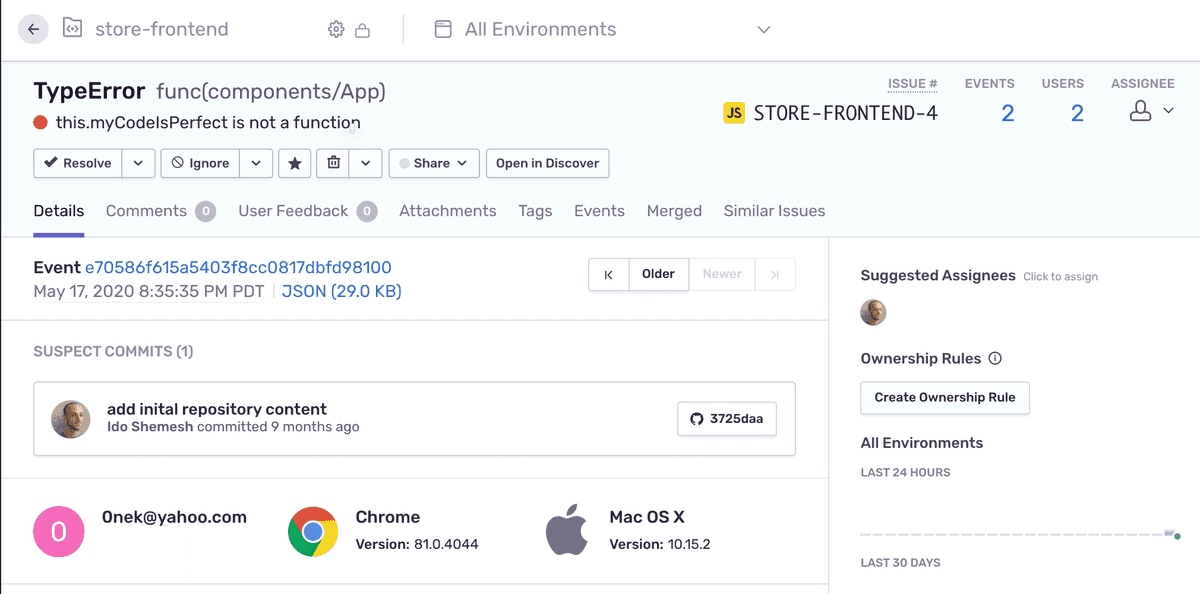
In the main area of the page, notice the "SUSPECT COMMITS" section now points to a commit that most likely introduced the error. You can click on the commit button to see the actual commit details on GitHub.
In the right side panel, under "Suggested Assignees", you'll see that the author of the suspect commit is listed as a suggested assignee for this issue.
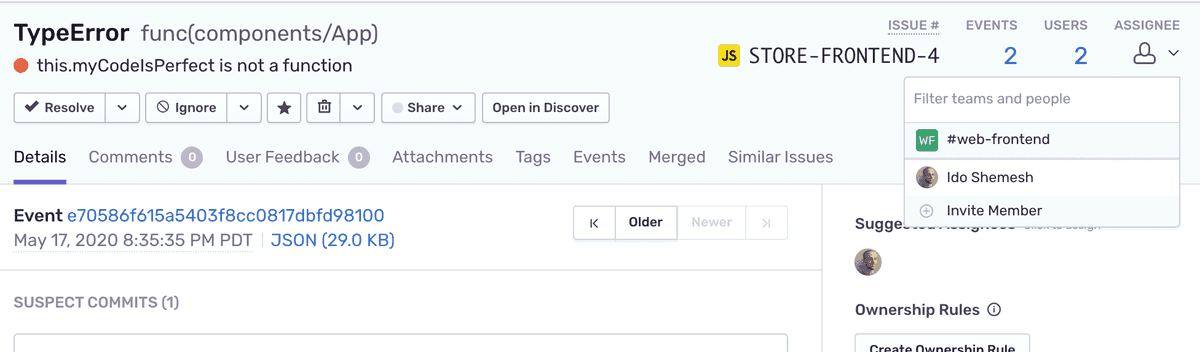
You can assign the suggested assignee to the issue by clicking on the icon. However, in this case, the commit originates in the repository upstream, and the suggested assignee is not part of your organization. Alternatively, you can manually assign the issue to other users or teams assigned to the project.
Click on the "ASSIGNEE" dropdown and select one of the project users or teams.
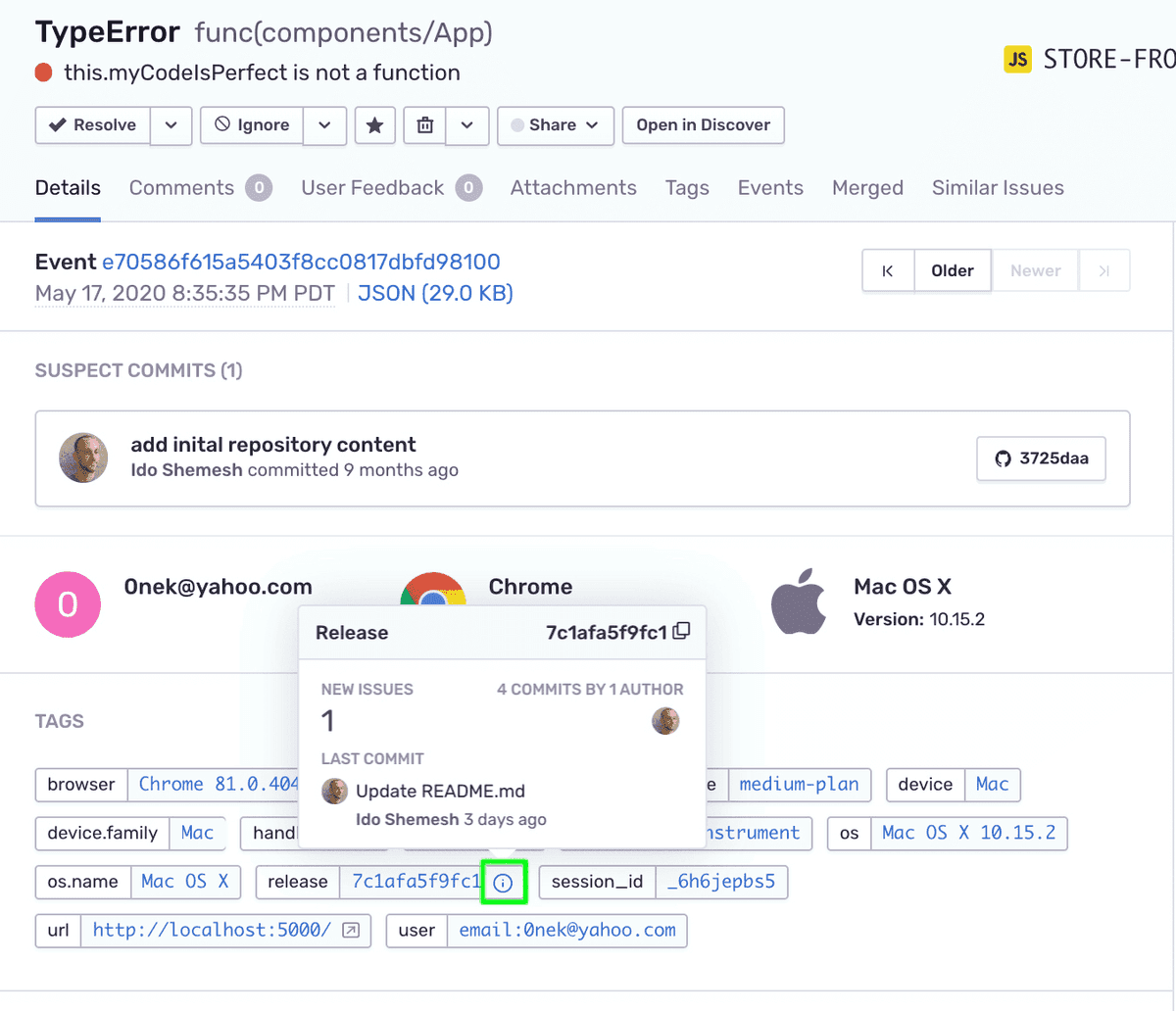
In the main area of the page, under "TAGS", find the
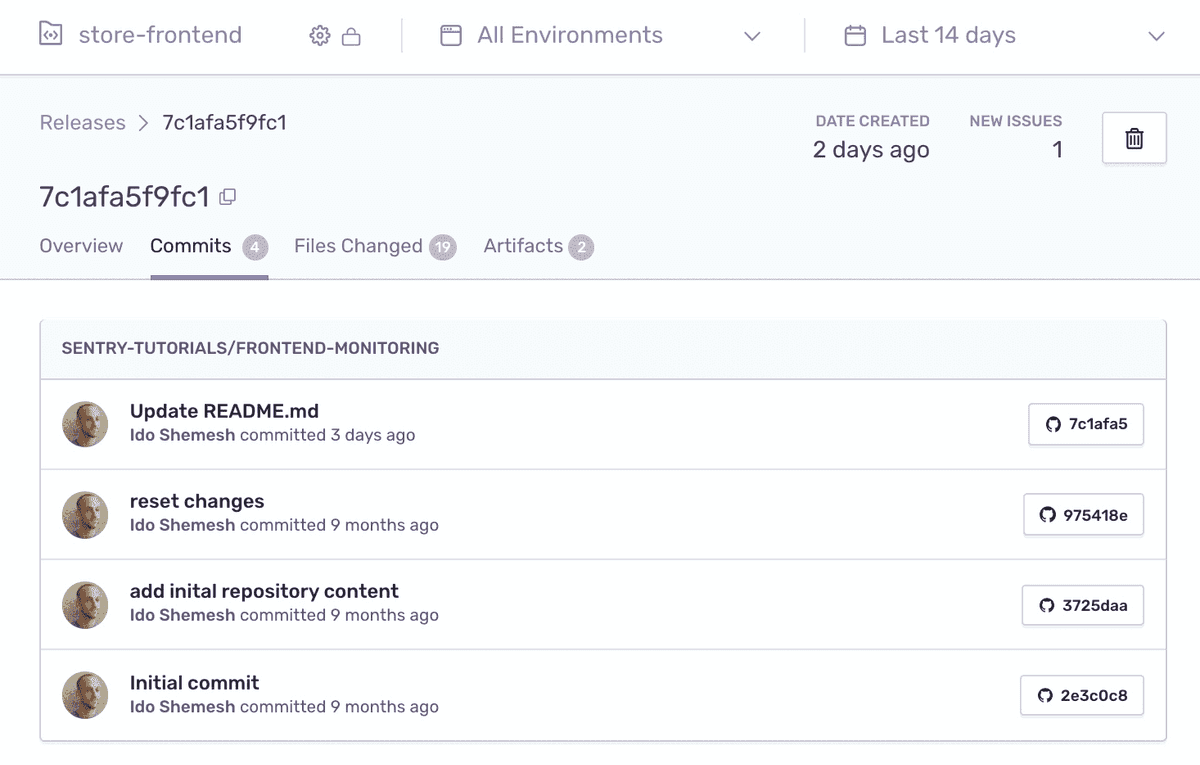
releasetag and hover over the "i" icon.In the popup that appears, notice the release now contains the commit data.
Click on the release "i" icon to open the Release Details page.
Select the "Commits" tab. Notice that release now contains the associated list of commits.
Step 4: Using Stack Trace Links
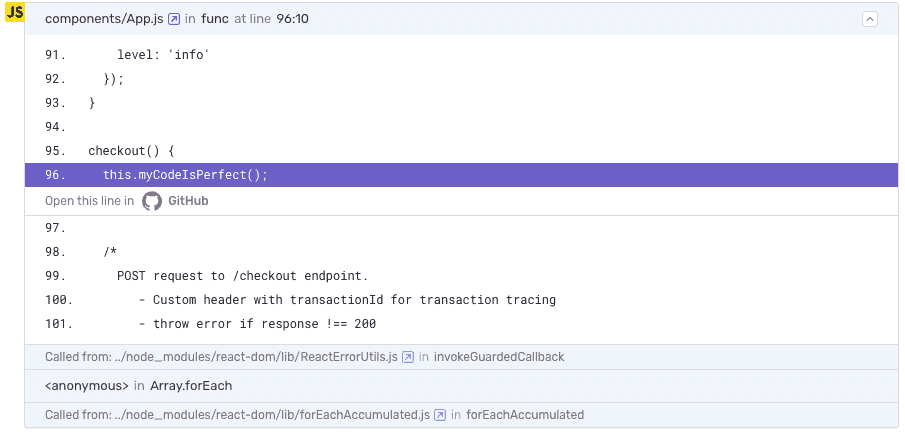
Stack trace links allows you to jump from a stack trace in sentry.io to the corresponding file in your source code provider. This is done by matching the file path in the stack trace to the file path in your source code provider.
Go to the Issue Details page for the error you generated in the previous step.
If the code mapping is set up correctly, in the stack trace you should see a link with "Open this line in GitHub":
More Information
Our documentation is open source and available on GitHub. Your contributions are welcome, whether fixing a typo (drat!) to suggesting an update ("yeah, this would be better").