Set Up Crons
Important
Sentry Cron Monitoring is currently in open beta and subject to change. Help us make it better by letting us know what you think. Respond on GitHub or write to us at crons-feedback@sentry.io.
Sentry Crons allows you to monitor the uptime and performance of any scheduled, recurring job. Once implemented, it'll allow you to get alerts and metrics to help you solve errors, detect timeouts, and prevent disruptions to your service.
Requirements
- Use our getting started guide to install and configure the Sentry Python SDK (min v1.17.0) for your recurring job.
- Create and configure your first Monitor.
Celery Beat Auto Discovery
Use the Celery integration to monitor your Celery periodic tasks and get notified when a task is missed (or doesn't start when expected), if it fails due to a problem in the runtime (such as an error), or if it fails by exceeding its maximum runtime.
First, set up your Celery beat schedule:
# tasks.py
from celery import Celery
from celery.schedules import crontab
app = Celery('tasks', broker='...')
app.conf.beat_schedule = {
'set-in-beat-schedule': {
'task': 'tasks.tell_the_world',
'schedule': crontab(hour='10', minute='15'),
'args': ("Some important message!", ),
},
}Initialize Sentry in the celeryd_init or beat_init signal. Make sure to set monitor_beat_tasks=True in CeleryIntegration:
# tasks.py
from celery import signals
import sentry_sdk
from sentry_sdk.integrations.celery import CeleryIntegration
#@signals.beat_init.connect
@signals.celeryd_init.connect
def init_sentry(**kwargs):
sentry_sdk.init(
dsn='https://examplePublicKey@o0.ingest.sentry.io/0',
integrations=[CeleryIntegration(monitor_beat_tasks=True)], # 👈
environment="local.dev.grace",
release="v1.0",
)Once Sentry Crons is set up, tasks in your Celery beat schedule will be auto-discoverable, and telemetry data will be captured when a task is started, when it finishes, and when it fails.
Start your Celery beat and worker services and see your tasks being monitored at https://sentry.io/crons/.
You don't need to create Cron Monitors for your tasks on Sentry.io, we'll do it for you.
Manual Task Monitoring
We provide a lightweight decorator to make monitoring individual tasks easier. To use it, add @sentry_sdk.monitor to your Celery task (or any function), then supply a monitor_slug of a monitor created previously on Sentry.io. Once this is done, every time the task (or function) is executed, telemetry data will be captured when a task is started, when it finishes, and when it fails.
Make sure the Sentry @sentry_sdk.monitor decorator is below Celery's @app.task decorator.
# tasks.py
from celery import Celery, signals
import sentry_sdk
from sentry_sdk.integrations.celery import CeleryIntegration
app = Celery('tasks', broker='...')
@signals.celeryd_init.connect
def init_sentry(**kwargs):
sentry_sdk.init(
dsn='https://examplePublicKey@o0.ingest.sentry.io/0',
integrations=[CeleryIntegration()],
environment="local.dev.grace",
release="v1.0",
)
@app.task
@sentry_sdk.monitor(monitor_slug='<monitor-slug>') # 👈 this is the new line.
def tell_the_world(msg):
print(msg)Connecting Errors to Cron Monitors
To link any exceptions captured during your job's lifecycle, use Sentry's context with your monitor slug.
sentry_sdk.set_context("monitor", {
"slug": "<monitor_slug>",
})Alerts
When your recurring job fails to check in (missed), runs beyond its configured maximum runtime (failed), or manually reports a failure, Sentry will create an error event with a tag to your monitor.
To receive alerts about these events:
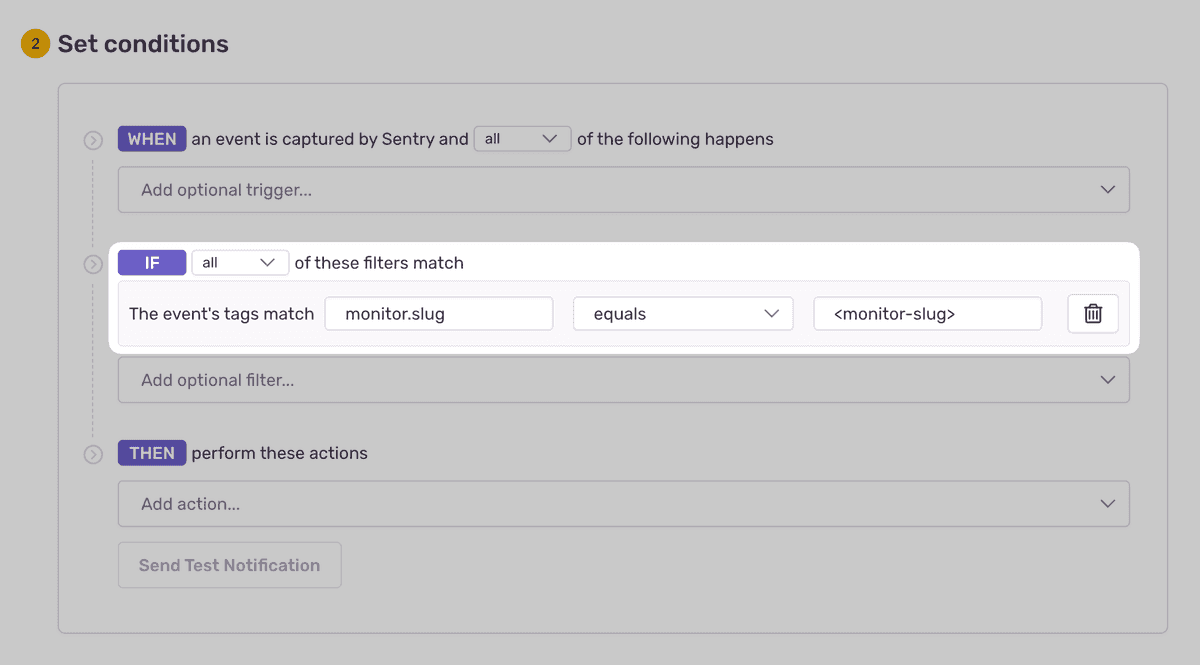
- Navigate to Alerts in the sidebar.
- Create a new alert and select "Issues" under "Errors" as the alert type.
- Configure your alert and define a filter match to use:
The event's tags match {key} {match} {value}.
Example: The event's tags match monitor.slug equals my-monitor-slug-here
Learn more in Issue Alert Configuration.
Our documentation is open source and available on GitHub. Your contributions are welcome, whether fixing a typo (drat!) to suggesting an update ("yeah, this would be better").
- Package:
- pypi:sentry-sdk
- Version:
- 1.22.1
- Repository:
- https://github.com/getsentry/sentry-python